
Proba-3: Precise Space Formation Flight
The European Space Agency's (ESA) Proba-3 mission has achieved a remarkable feat: autonomous, millimeter-accurate formation flying in space. This groundbreaking accomplishment surpasses all previous attempts at synchronized satellite maneuvers, setting a new standard for precision in orbital choreography.
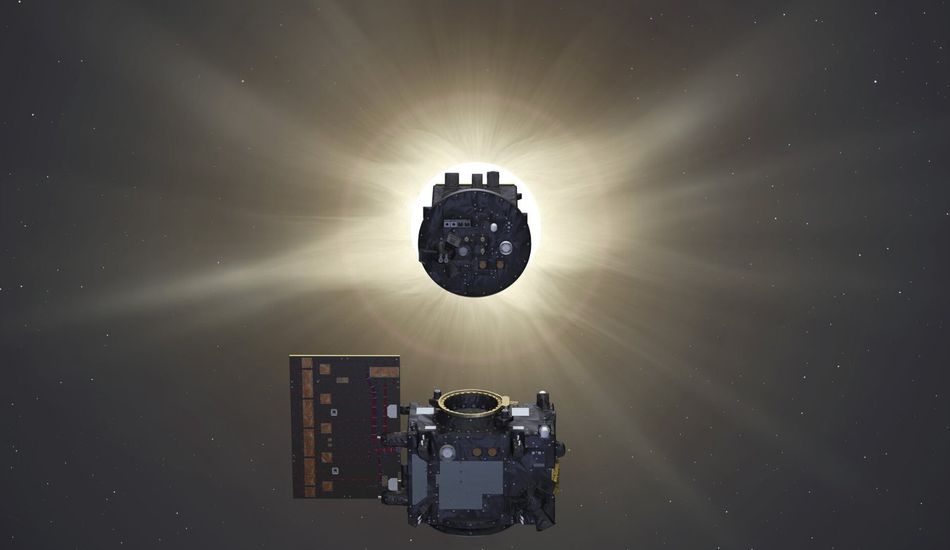
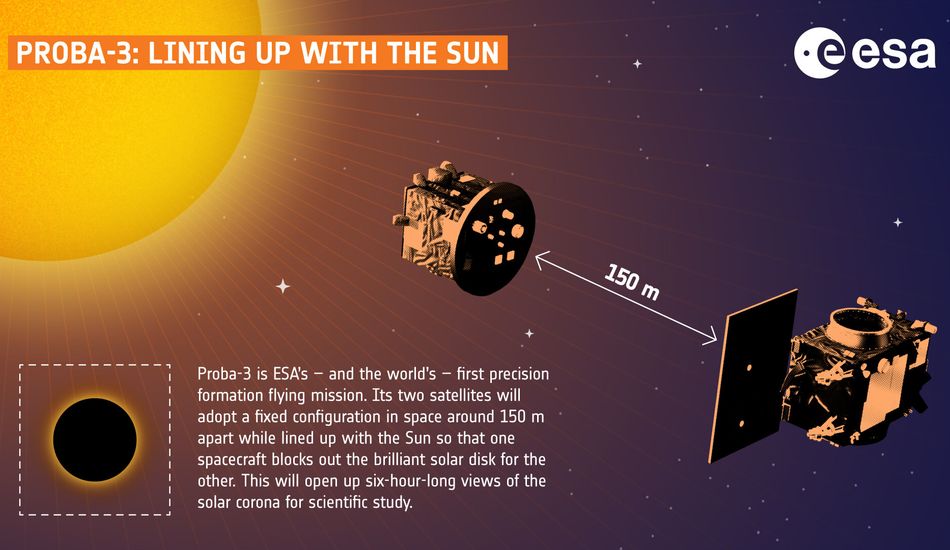
Comprising two satellites—the Occulter and the Coronagraph—Proba-3 operates in a highly elliptical orbit, maintaining a consistent 150-meter distance. This configuration mimics a single, large instrument, leveraging the benefits of space's environment to gather more data than would be possible otherwise. The unique goal, however, lies in the precise alignment of these satellites.
A Precise Dance in Space
The mission's objective is to enable the Occulter to block the sun's glare, allowing the Coronagraph to capture images of the sun's corona—its faint outer atmosphere. To achieve this, the satellites must maintain an incredibly precise alignment. The 1.4-meter disc on the Occulter casts a 5-centimeter shadow on the Coronagraph, sufficient to protect the latter from the sun's intense light.
After initial ground-based positioning, an autonomous system takes over. Cameras, LEDs, and laser rangefinders work in tandem with a sophisticated algorithm to fine-tune the satellites' positioning. The Fine Lateral and Longitudinal Sensor (FLLS), a laser-based system, continuously monitors and adjusts the alignment, ensuring the satellites remain precisely positioned. This same technology will be crucial for future missions like LISA, a next-generation gravitational wave observatory.
This millimetric precision in both range and lateral position represents an unprecedented achievement. The success of Proba-3 not only paves the way for groundbreaking solar observations but also validates the technology needed for complex, multi-spacecraft missions of the future. The mission's success demonstrates the potential for future advancements in astronomy and space exploration.
1 Image of Space Formation Flight:

Source: Gizmodo