Solar Orbiter Reveals Suns Pole for First Time
The Solar Orbiter, a spacecraft dedicated to observing our sun, has achieved a significant milestone. Through a strategic maneuver utilizing a Venus flyby, it has adjusted its orbit to gain an unprecedented view of the sun's polar regions. This unique perspective has enabled the capture of the first-ever images of the sun's pole, a feat that marks a significant advancement in our understanding of solar activity.
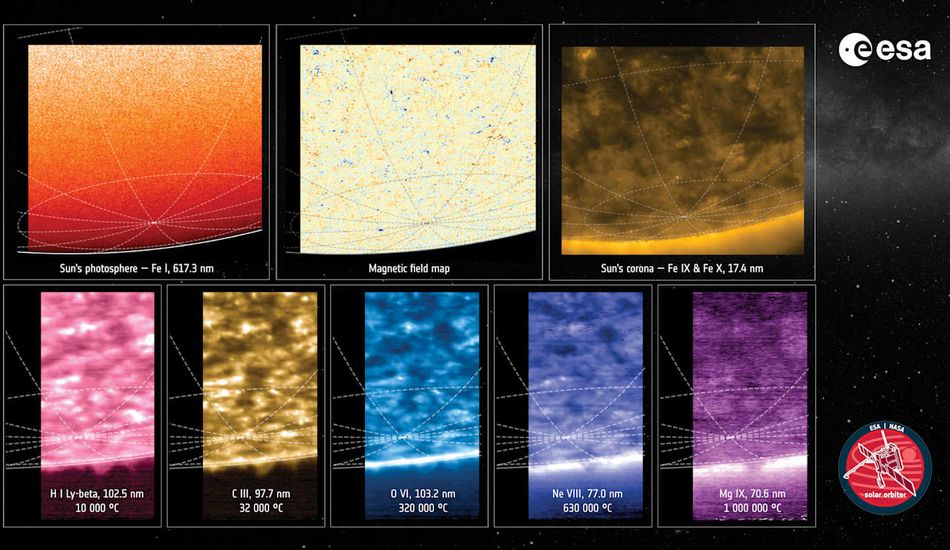
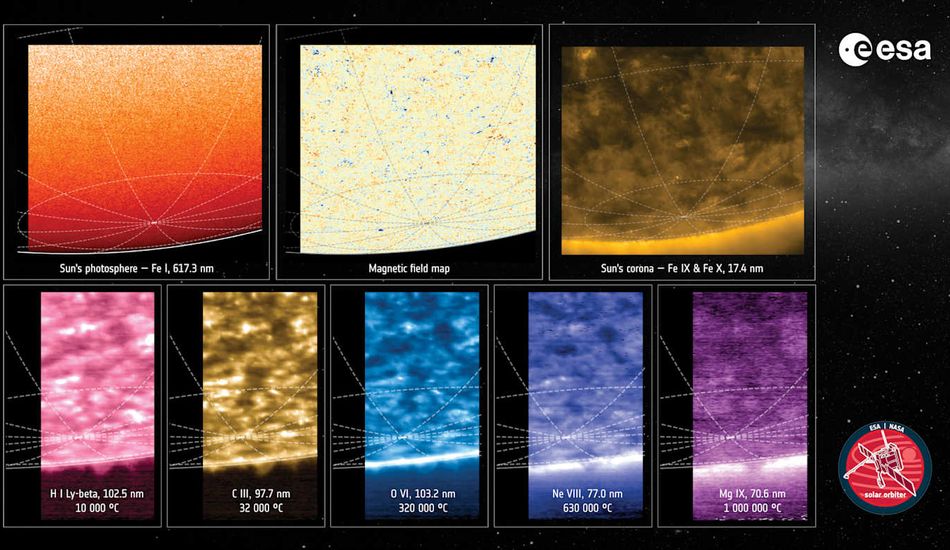
Unveiling the Sun's Polar Magnetic Field
The images, obtained in March 2024, reveal a surprisingly complex magnetic field at the sun's south pole. Unlike a simple, uniform field, the images captured by the Polarimetric and Helioseismic Imager (PHI) show a mixture of both north and south polarity magnetic fields. This chaotic state is a temporary phenomenon, occurring only during the sun's solar maximum — a period of heightened activity during which the sun's magnetic field is about to flip.
This observation is crucial because the sun's magnetic field flips approximately every 11 years, a process not yet fully understood. The data gathered by the Solar Orbiter may provide vital clues to unlocking the mysteries behind these periodic reversals. The process of the field settling back to a more stable, ordered state after the flip is expected to take several years.
Beyond Magnetic Fields: Studying Solar Winds
The Solar Orbiter's capabilities extend beyond mere imaging. The Spectral Imaging of the Coronal Environment (SPICE) instrument has been utilized to conduct Doppler measurements, charting the velocity of solar material. These measurements provide crucial insights into the dynamics of solar winds, and how the sun ejects particles into space. This data is fundamental to understanding the mechanisms driving space weather and its potential impact on Earth.
The integrated approach combining high-resolution imaging and velocity mapping represents a significant step forward in solar physics, paving the way for a deeper comprehension of the sun's complex behaviour and its influence on our solar system.
1 Image of Solar Pole Images:

Source: Engadget